Answer : Magnesium is a very reactive metal. If kept open in the air, it reacts with oxygen to form magnesium oxide (MgO) which sits on the metal surface. Gradually, the magnesium oxide layer envelops the metal and cuts off its contact with atmospheric air. In the absence of oxygen, the burning of magnesium metal cannot happen. Hence, the magnesium ribbon should be cleaned properly before burning in air.
Get all the answers to NCERT class 10 science Chapter 1 Questions HERE »
Explain – Why Should a Magnesium Ribbon be Cleaned
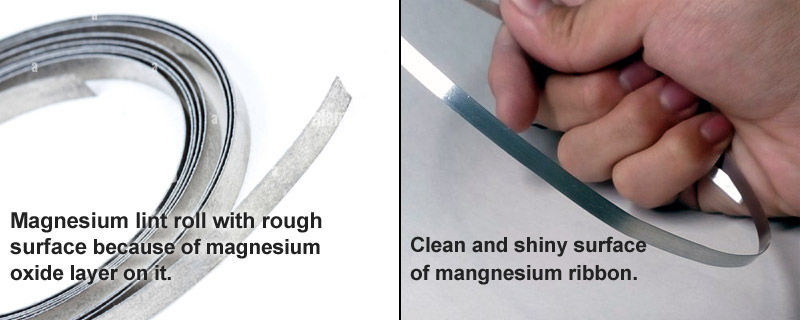
Magnesium is a highly reactive metal. When kept open and exposed to air, it naturally reacts with oxygen (present in the air) to form magnesium oxide (MgO) which gets collected on the metal surface. For this reason, the magnesium ribbon, possibly kept in the lab for a long time, might be covered with the magnesium oxide layer which is a very stable compound.
This layer works as a shield for the metal as it cuts off the contact of magnesium ribbon from the atmospheric air. This is why the ribbon doesn’t get enough oxygen to burn properly in the air. The layer prevents any kind of further reaction of the metal. Hence, it is advised that you should always clean the magnesium ribbon by rubbing it with sandpaper before you perform an experiment on it.
After the proper cleaning of the magnesium ribbon, the unwanted layer of magnesium oxide (MgO) gets removed and the shiny metal surface becomes clearly visible. Now, it also comes in direct contact with the surrounding atmosphere. Since the magnesium ribbon is fully exposed to air, it will easily react with the oxygen present in the air and burn quickly to make your experiment successful.
NCERT » Class 10 » Science » Chapter 1
Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air Explain
Magnesium is a special kind of metal that reacts easily with the air around it. When it’s left out in the open, it combines with the oxygen in the air to create a substance called magnesium oxide. This substance forms a layer on the surface of the metal, and it looks like a powdery white coating. This layer is very strong and doesn’t let the metal come into contact with the air.
This layer of magnesium oxide acts like a protective shield for the metal. It stops the metal from getting in touch with the air, which means it can’t burn properly. That’s why when you have a piece of magnesium ribbon that has been sitting around for a long time, it won’t burn easily. The layer of magnesium oxide prevents the metal from reacting any further. So, before you start any experiments with magnesium, it’s important to clean the ribbon by rubbing it with sandpaper.
When you clean the ribbon, you remove the layer of magnesium oxide, and the shiny metal underneath becomes visible. Now, the metal is in direct contact with the air again. Since there is no longer a layer of magnesium oxide blocking it, the ribbon can easily react with the oxygen in the air. It will burn quickly, which is important for the success of your experiment.
Remember, always take care and follow proper safety procedures when working with magnesium or any other chemicals.
The Short Answer
Magnesium is a special kind of metal that reacts easily with oxygen in the air. When magnesium is exposed to air, it combines with the oxygen to create a layer on its surface. This layer is made up of a substance called magnesium oxide. It forms like a covering on the metal, preventing it from coming into direct contact with the air around it.
When the metal is covered by this layer of magnesium oxide, it cannot burn properly because it needs oxygen to burn. So, if you want to burn a piece of magnesium ribbon, you need to make sure it’s clean and free from this layer. That’s why it’s important to clean the magnesium ribbon thoroughly before attempting to burn it in the air.
