Find the Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 on our website with all the questions and answers especially written for class 10 students. You will know about Ch 9 Light – Reflection and Refraction, learn its concepts, and get important tips 🔥 on how to write (1) precise answers (2) without using unnecessary words (3) within ideal length. You will access all of this information for FREE in addition to class 10 science NCERT solutions chapter 9.
Ch 9 • Light – Reflection and Refraction

Use this link — 🌐 10.solutionsir.com for any kind of help in 10th class 2023-24. Click Here for » All Chapters: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Exercise – Our eyes are organs that allow us to see a variety of objects around us. An object reflects light that falls on it. This reflected light, when received by our eyes, enables us to see things. In the ninth chapter “Light – Reflection and Refraction” (Chapter 9 Science Class 10), we shall study the phenomena of reflection and refraction of light, and their application in real life situations.
Chapter 9 Light : Reflection and Refraction – Important Points: Mirrors and lenses form images of objects. Images can be either real or virtual, depending on the position of the object. The reflecting surfaces, of all types, obey the laws of reflection. The refracting surfaces obey the laws of refraction. The speed of light is different in different media. The refractive index of a transparent medium is the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to that in the medium. In case of a rectangular glass slab, the refraction takes place at both air-glass interface and glass-air interface. The emergent ray is parallel to the direction of incident ray.
Special Note: 👉 Click the “Prepare” button to know, how to prepare Light chapter 9 for exams. Get more helpful information, watch explanation videos and pay attention to handwritten version of our answer to score 💯 good marks in class 10 Science NCERT solutions Chapter 9. You will get everything that you need to prepare a question thoroughly.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9
Table of Contents
Page 142
EX 1 – Chapter no 9 – Page 142 Solutions
Question 1: Define the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Answer: Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from the mirror. This point is called the principal focus of the concave mirror.
Question 2: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
Answer: Focal length = 1/2 × Radius of curvature
On putting values, Focal length, f = 1/2 × 20 cm = 10 cm
Therefore, the focal length of the given spherical mirror is 10 cm.
Question 3: Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Answer: Concave mirror.
Question 4: Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Answer: We prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles because it gives a wider field of view, which allows the driver to see most of the traffic behind him.
End of Page no 142 solutions – In text exercise 1 – chapter number 9 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9.
Page 145
EX 2 – Chapter no 9 – Page 145 Solutions
Question 1: Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Answer: Radius of curvature (R) = 2 × Focal length (f)
⇒ f = R/2
Or, f = 32/2 = 16
Therefore, the focal length of the given convex mirror is 16 cm.
Question 2: A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
Answer: Distance of the object in front of mirror, u = -10cm
Distance of the image from mirror, v = ?
Now, magnification of a spherical mirror, m = hi/ho = -v/u
In this case, m = -3h/h = -v/u
Or, 3 = v/-10
Or, v = -30 cm
Therefore, the location of the image from the mirror is at a distance of 30cm and the nature of the image is inverted.
End of Page no 145 solutions – In text exercise 2 – chapter number 9 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9.
Page 150
EX 3 – Chapter no 9 – Page 150 Solutions
Question 1: A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
Answer: In this case, the ray of light bends towards the normal because it travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium.
Question 2: Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 ms−1.
Answer: Refractive index of a medium = Speed of light in vacuum / Speed of light in the medium
Or, Speed of light in a medium = Speed of light in vacuum / Refractive index of the medium
In this case, the given medium is a glass having refractive index 1.50.
So, the speed of light in the glass = 3 × 108/1.50 = 2 × 108 m/s
Question 3: Find out, from Table 9.3, the medium having highest optical density. Also find the medium with lowest optical density.
Answer: The medium with highest optical density is diamond, which has the highest refractive index (= 2.42).
And, the medium with lowest optical density is air, which has the lowest refractive index (= 1.0003).
Question 4: You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the light travel fastest? Use the information given in Table 9.3.
Answer: The speed of light is inversely proportional to the refractive index. So, it can be deduced that the light travels faster in water as compared to kerosene and turpentine because the refractive index of water is lower than that of kerosene and turpentine.
Question 5: The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
Answer: The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. This means that the speed of light in diamond will reduce by a factor of 2.42 as compared to its speed in air.
End of Page no 150 solutions – In text exercise 3 – chapter number 9 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9.
Page 158
EX 4 – Chapter no 9 – Page 158 Solutions
Question 1: Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens.
Answer: Dioptre is the SI unit of power of lens denoted by the letter D. 1 dioptre can be defined as the power of a lens of focal length 1 metre.
Question 2: A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size of the object? Also, find the power of the lens.
Answer: It is given that the image of the needle is formed at a distance of 50 cm from the convex lens. Hence, the needle is placed in front of the lens at a distance of 5 cm.
Object distance, u = −50 cm
Image distance, v = 50 cm
Focal length = f
According to the lens formula, 1/v − 1/u = 1/f
In this case, 1/f = 1/50 − 1/(−50) = 1/50 + 1/50 = 1/25
Or, f = 25cm = 0.25 m
Power of the lens, P = 1/f = 1/0.25 = +4 D
Therefore, the power of the given lens is +4 D.
Question 3: Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
Answer: Focal length of concave lens (f) = 2 m
So, power of lens (P) = 1/f = 1/ (−2) = −0.5D
End of Page no 158 solutions – In text exercise 4 – chapter number 9 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9.
Page 159
Chapter End Questions – Page 159 Solutions
Question 1: Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
Answer: (d) Clay.
Question 2: The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
Answer: (d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Question 3: Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
Answer: (b) At twice the focal length.
Question 4: A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of −15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be
Answer: (a) both concave.
End of Page no 159 solutions – Chapter 9 Exercise 5 – Chapter end exercise. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9.
Page 160
Chapter End Exercises – Page 160 Solutions
Question 5: No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
Answer: (d) either plane or convex.
Question 6: Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
Answer: (c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm.
Question 7: We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Answer: A concave mirror gives an erect image when the object is placed between the focus F and the pole P of the concave mirror, that is between 0 and 15 cm from the mirror. The image thus formed will be virtual, erect and larger than the object.
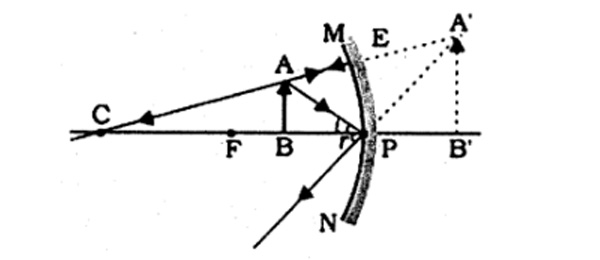
Question 8: Name the type of mirror used in the following situations. Support your answer with reason.
(a) Headlights of a car.
Answer: Concave mirrors are used in the headlights of cars because they can produce a powerful parallel beam of light when the light source is placed at their principal focus
(b) Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle.
Answer: Convex mirrors are used as side-view mirrors and rear-view mirrors in vehicles because convex mirrors provide the largest field of view.
(c) Solar furnace.
Answer: Concave mirror is used in a solar furnace because it concentrates the parallel rays of the sun at a principal focus.
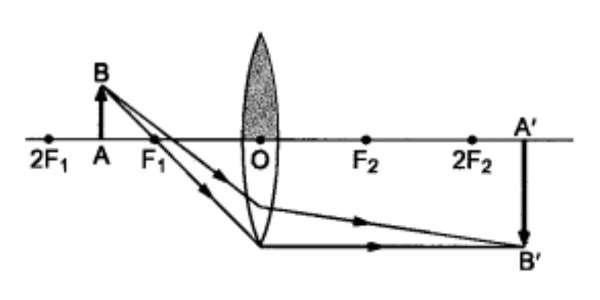
Question 9: One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Answer: A convex lens forms a complete image of an object, even if its one half is covered with black paper. It can be explained by considering the following two cases.
Case 1 – When the upper half of the lens is covered. A ray of light coming from the object will be refracted by the lower half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the following figure.
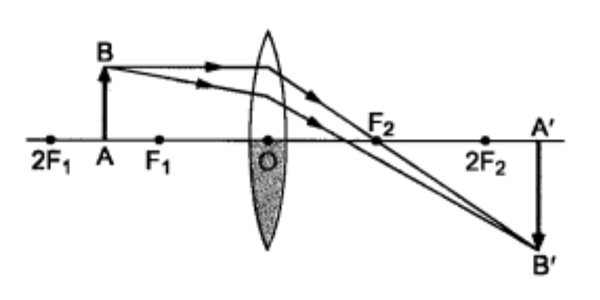
Case 2 – When the lower half of the lens Is covered. A ray of light coming from the object is refracted by the upper half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the given figure.
Question 10: An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Answer: Height of the object, ho = 5 cm
Distance of the object form converging lens, u = −25 cm
Focal length of converging lens, f = 10 cm
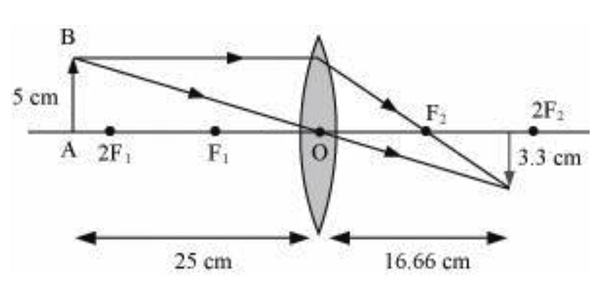
1/v = 1/f + 1/u = 1/10 − 1/25 = 15/250
v = 250/15 = 16.66 cm
Also, for a converging lens, hi / ho = v/u
hi = v/u × ho = 50 × 5 / 3 × (-25) = 10/−3 = −3.3 cm
Therefore, the image is inverted and formed at a distance of 16.7 cm behind the lens and measures 3.3 cm. The ray diagram is shown below.
Question 11: A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Answer: Focal length of concave lens, f = −15 cm
Image distance, v = −10 cm
Apply lens formula, 1/v − 1/u = 1/f
Or, 1/u = 1/v − 1/f = −1/10 − 1/−15
⇒ 1/u = −1/10 + 1/15 = −5/150
So, u = −30 cm
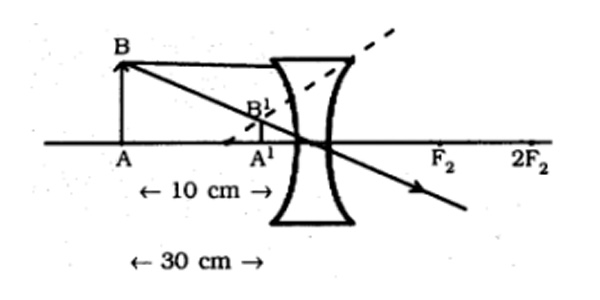
As shown in the above ray diagram, the negative value of u indicates that the object is placed 30 cm in front of the lens.
Question 12: An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
Answer: Object distance, u = −10 cm
Focal length, f = +15 cm
Image distance, ν = ?
Apply mirror formula, 1/u + 1/v = 1/f
Or, 1/v = 1/f − 1/u
⇒ 1/v = 1/+15 − 1/(−10) = (2 + 3)/30 = 1/6
Or, v = 6 cm
Therefore, image distance, ν = + 6 cm. Hence, a virtual image is formed at a distance of 6 cm behind the mirror.
Magnification (m) = −v/u = −6/−30 = 1/5
The positive value of m shows that the image is erect and its value, being less than 1, shows that image is smaller than the object. Therefore, the image is virtual, erect and diminished.
Question 13: The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does this mean?
Answer: Magnification m, being equal to 1, shows that the size of the image is the same as that of the object. Also, a positive sign of m indicates that an erect image is formed.
Question 14: An object 5.0 cm in length is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image, its nature and size.
Answer: Object distance, u = −20 cm
Object height, h = 5 cm
Radius of curvature, R = 30 cm
Radius of curvature = 2 × Focal length
R = 2×f
f = 15 cm
Apply mirror formula, 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
Or, 1/v = 1/f − 1/u = 1/15 + 1/20 = 7/60
Or, v = 8.57 cm
The positive value of v indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror.
Magnification, m = image distance/object distance
Or, m = −8.57/−20 = 0.428
The positive value of magnification indicates that the image formed is virtual.
Now, magnification = Height of the image/Height of the object
Or m = h’/h
⇒ h’ = m × h = 0.428 × 5 = 2.14 cm
The positive value of image height indicates that the image formed is erect. Therefore, the image formed is virtual, erect and smaller in size.
Question 15: An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focussed image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Answer: Object distance, u = 27 cm
Object height, h = 7 cm
Focal length, f = −18 cm
Apply mirror formula, 1/v − 1/u = 1/f
Or, 1/v = 1/f + 1/u = 1/−18 + 1/27 = −1/54
Or, v = −54 cm
So, the screen should be placed at a distance of 54 cm in front of the given mirror.
Magnification m = image distance/object distance
Or, m = −54/27 = −2
The negative value of magnification indicates that the image formed is real.
Now, magnification (m) = Height of the image/Height of the object
Or, m = h’/h
⇒ h’ = m × h = 7 × (-2) = -14 cm
The negative value of image height indicates that the image formed is inverted.
Question 16: Find the focal length of a lens of power – 2.0 D. What type of lens is this?
Answer: Power of lens (P) = 1/f
P = −2D
f = −1/2 = −0.5 m
A concave lens has a negative focal length. Therefore, it is a concave lens.
Question 17: A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
Answer: Power of lens (P) = 1/f
P = 1.5D
f = 1/1.5 = 10/15 = 0.66 m
A convex lens has a positive focal length.
Therefore, it is a convex lens or a converging lens.
End of Page no 160 solutions – Ch 9 Ex 5 – Chapter end question answer. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9.

