Find the Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 on our website with all the questions and answers especially written for class 10 students. You will know about Ch 6 Control and Coordination, learn its concepts, and get important tips 🔥 on how to write (1) precise answers (2) without using unnecessary words (3) within ideal length. You will access all of this information for FREE in addition to class 10 science NCERT solutions chapter 6.
Ch 6 – Control and Coordination

Use this link — 🌐 10.solutionsir.com for any kind of help in 10th class 2023-24. Click Here for » All Chapters: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Exercise – If you observe keenly about your movements like talking, walking etc. you will notice that your movements are carefully controlled. When you want to talk to your elders, you try to behave in manner rather than shouting loudly. Clearly, the movement to be made depends on the event that is triggering it. So, living organisms must have systems providing control and coordination. ⚡ In the sixth chapter “Control and Coordination” (Chapter 6 Science Class 10), we will learn about specialised tissues which are used to provide these control and coordination activities.
Chapter 6 Control and Coordination – Important Points: Control and coordination are the functions of the nervous system and hormones in our bodies. The nervous system gets information from our sense organs and acts through our muscles. Hormones produced in one part of an organism move to another part to achieve the desired effect.
Special Note: 👉 Click the “Prepare” button to know, how to prepare Control and Coordination chapter for exams. Get more helpful information, watch explanation videos and pay attention to handwritten version of our answer to score 💯 good marks in class 10 Science NCERT solutions Chapter 6. You will get everything that you need to prepare a question thoroughly.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6
Table of Contents
Page 105
EX 1 – Chapter no 6 – Page 105 Solutions
Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer: Difference between a reflex action and walking —
- Reflex action is performed automatically while walking is a response to the information transmitted by nerves to muscles of the legs. In this case, thinking is involved.
- Reflex action is controlled and coordinated by the spinal cord while walking is done by leg muscles which take instructions from the brain.
- Reflex action is an involuntary action and walking is a voluntary action.
Question 2: What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer: At synapse between two neurons, a chemical substance is produced at the end of the axon of one nerve cell that reaches to the other nerve cell through the dendrite. Thus, information is transmitted from one nerve cell to another nerve cell by synapse.
Question 3: Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer: Cerebellum maintains posture and equilibrium of the body.
Question 4: How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Answer: When the scent of an agarbatti reaches our nose, it is detected by olfactory receptors. It is interpreted by the forebrain by combining it with the information received from other receptors.
Question 5: What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer: Reflex actions are generated in the spinal cord and the information also reaches the brain. This helps the brain to record this event and remember it for future use. Brain helps the person to get awareness of the stimulus and prevent himself from that situation again.
End of Page no 105 solutions – In text exercise 1 – chapter number 6 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6.
Page 108
EX 2 – Chapter no 6 – Page 108 Solutions
Question 1: What are plant hormones?
Answer: Plant hormones are the organic substances produced at certain sites of the plant and are translocated to other parts based on the requirement. Plant hormones help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the environment.
Question 2: How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer: The sensitive plant Mimosa pudica or “touch me not” moves its leaves in reaction to touch or contact stimuli. This happens because of differences in turgor pressures in leaf cells. Growth has no bearing on this movement. Movement of a shoot towards light occurs as a result of growth in one direction. Hence, this kind of movement depends on growth.
Question 3: Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer: Auxin is a plant hormone that helps in the growth of the stem.
Question 4: How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer: When the tip of a tendril touches a support, then the auxins present in its tip moves towards the tip which is away from the support. Auxins promote growth. So, due to more auxins in it, the side of the tendril away from the support grows faster than the side which is in contact with the support and makes the tendril twirl around the support.
Question 5: Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer: Hydrotropism is the process of growth or movement of roots towards the source of water. We can observe the growth of plants (when water is present) using an experiment as explained below —
Experiment – Take two beakers A and B. In beaker A, add moist soil and sow the seeds. In beaker B, add dry soil in one part and moist soil in another part and sow the seeds. Also, place a small beaker of water just adjacent to it. Keep it for some time so that the plants can grow.
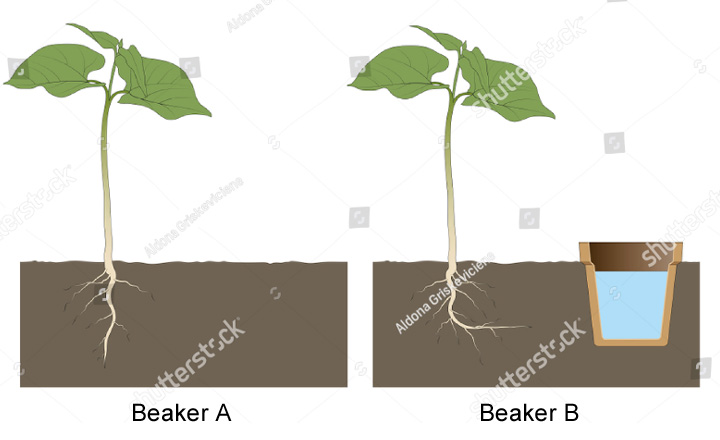
Observation – It was found that in beaker A, due to the presence of moist soil, plants will grow normally and roots will be straight. In beaker B, it was observed that the plant grows towards the water as shown in the above figure.
Conclusion – This experiment states that the plants move and grows towards the source of water, hence plants show hydrotropism.
End of Page no 108 solutions – In text exercise 2 – chapter number 6 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6.
Page 111
EX 3 – Chapter no 6 – Page 111 Solutions
Question 1: How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer: Chemical coordination in animals takes place through the hormone system as well as the nervous system which is called the endocrine system. Endocrine glands secrete animal hormones directly into the blood that reach to the specific cells. A special type of molecules are present on the surface of cells to detect these hormones. These cells act according to the information that a particular hormone carries.
Question 2: Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer: Usage of Iodized salt is advisable to avoid the deficiency of Iodine. If the intake of iodine is low, the release of thyroxine from the thyroid gland will be decreased. This affects fat, carbohydrate and protein metabolism.
Question 3: How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer: Adrenaline is a hormone secreted when a person is frightened or mentally disturbed. When Adrenaline reaches the heart, heartbeat will increase to increase blood supply to our muscles. Adrenaline also increases the breathing rate because of contraction of diaphragm and the rib muscles. Adrenaline rush also increases blood pressure and allows entry of more glucose into blood. These altogether occur when our body responds to secretion of adrenaline into our blood.
Question 4: Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer: Insulin is a hormone which is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels. If it is not secreted in proper amounts, the sugar level in the blood rises causing many harmful effects.
End of Page no 111 solutions – In text exercise 3 – chapter number 6 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6.
Page 112
Chapter End Questions – Page 112 Solutions
Question 1: Which of the following is a plant hormone?
Answer: (d) Cytokinin.
Question 2: The gap between two neurons is called a
Answer: (b) synapse.
Question 3: The brain is responsible for
Answer: (d) all of the above.
Question 4: What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer: Receptors are specialised cells located in our sense organs like ear, nose, skin, tongue and eyes. The function of receptors is to detect information from the environment. For example, olfactory receptors detect smell. If receptors do not work properly, the information obtained from the environment will be delayed to reach the spinal cord or brain. In this situation, the response to the environmental stimulus will be delayed causing harm to the body. For example, if skin receptors are damaged, and one accidentally touches a hot object, then his/her hands might get burned as the damaged receptor cannot perceive the external stimuli of heat and pain.
Question 5: Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Answer: Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system. The three main parts of a neuron are axon, dendrite and cell body, as shown below —
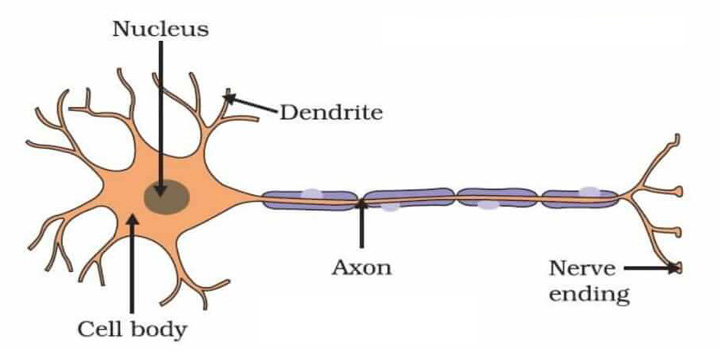
Functions of the three parts of a neuron —
Axon – It conducts messages away from the cell body.
Dendrite – It receives information from axon of another cell and conducts the messages towards the cell body.
Cell body – It contains nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles. It is mainly concerned with the maintenance and growth.
Question 6: How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer: Phototropism occurs due to increased auxin on the dark side and decreased auxin on the illuminated side. Because of the presence of more auxin, the leaf in the darker side grows faster causing it to bend towards the source of light.
Question 7: Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer: Signals coming from the nerves as well as the signals coming to the receptors will be disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury.
Question 8: How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer: Chemical coordination in plants takes place with the help of plant hormones. In most of the regions where division takes place stimuli cells secrete chemical compounds. These substances identify the information by stimulating the other nearby cells and communicating the information.
Question 9: What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Answer: The maintenance of the body functions in response to changes in the body by working together of various integrated body systems is known as coordination. All the movements that occur in response to stimuli are carefully coordinated and controlled. In animals, the control and coordination movements are provided by nervous and muscular systems. The nervous system sends messages to and away from the brain. The spinal cord plays an important role in the relay of messages. In the absence of this system of control and coordination, our body will not be able to function properly. For example, when we accidentally touch a hot utensil, we immediately withdraw our hand. In the absence of nerve transmission, we will not withdraw our hand and may get burnt.
Question 10: How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Answer: Involuntary actions occur immediately without any thinking or any processing by the brain while reflex actions are an immediate response to an event which does not require any processing by the brain. Also, involuntary actions are controlled by the mid and hind brain while reflex actions are controlled by the spinal cord. Examples of involuntary actions are breathing and blinking of eyes while examples of reflex actions are sneezing, coughing and closing of eyes when a bright light hits our eyes.
Question 11: Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer: Comparison between nervous mechanism and hormonal mechanism in animals —
(i) Nervous mechanism is a fast process and hormonal mechanism is a slow process.
(ii) Nervous mechanism affects arteries and glands while hormonal mechanism affects the target organ.
(iii) Nervous mechanism transmits in electrochemical form and hormonal mechanism transmits in chemical form.
(iv) Nervous mechanism does not control metabolism while hormonal mechanism controls metabolism.
(v) Growth is not affected by nervous mechanism while growth gets affected by hormonal mechanism.
Question 12: What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Answer: Sensitive plants show movements in leaves when sudden loss of water occurs in the pad-like swelling at the base of all the leaves. Movements like getting drooped and folded are observed. On the contrary, movement of legs in humans is caused by the pull in leg muscles on the leg bones.
End of Page no 112 solutions – Chapter 6 Exercise 4 – Chapter end exercise. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6.
Ch 6 Ex 4 – Chapter end question answer.

