Find the Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 on our website with all the questions and answers especially written for class 10 students. You will know about Ch 5 Life Processes, learn its concepts, and get important tips 🔥 on how to write (1) precise answers (2) without using unnecessary words (3) within ideal length. You will access all of this information for FREE in addition to class 10 science NCERT solutions chapter 5.
Ch 5 – Life Processes

Use this link — 🌐 10.solutionsir.com for any kind of help in 10th class 2023-24. Click Here for » All Chapters: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Exercise – Can you tell the difference between what is alive and what is not alive? You can answer this if you have studied in earlier classes that living organisms are well-organised structures. You must know that the maintenance functions of living organisms do not stop even when they are asleep. ⚡ In the fifth chapter “Life Processes” (Chapter 5 Science Class 10), we will learn about the life processes which are responsible for performing these maintenance jobs.
Chapter 5 Life Processes – Important Points: Maintenance of life requires processes like nutrition, respiration, transport of materials within the body and excretion of waste products. In human beings, the food eaten is broken down by various steps along the alimentary canal and the digested food is absorbed in the small intestine to be sent to all cells in the body. Autotrophic nutrition involves the intake of simple inorganic materials from the environment while Heterotrophic nutrition involves the intake of complex material prepared by other organisms.
Special Note: 👉 Click the “Prepare” button to know, how to prepare Life Processes chapter for exams. Get more helpful information, watch explanation videos and pay attention to handwritten version of our answer to score 💯 good marks in class 10 Science NCERT solutions Chapter 5. You will get everything that you need to prepare a question thoroughly.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5
Table of Contents
Page 81
EX 1 – Chapter no 5 – Page 81 Solutions
Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans?
Answer: Multi-cellular organisms like humans have very big bodies and all the body cells are not in direct contact with the surrounding environment. Because of these two reasons, diffusion is insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms.
Question 2: What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Answer: The most essential criteria used to decide whether something is alive is the presence of life processes. However, visible actions like breathing, growth and movement are usually used to determine whether something is alive or not.
Question 3: What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
Answer: Heterotrophs use food, and autotrophs use carbon dioxide, minerals, water and all organisms use oxygen (for respiration) as raw materials. All these outside raw materials are used for respiration.
Question 4: What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Answer: Life processes such as respiration, digestion, excretion, circulation and transportation are essential for maintaining life.
End of Page no 81 solutions – In text exercise 1 – chapter number 5 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5.
Page 87
EX 2 – Chapter no 5 – Page 87 Solutions
Question 1: What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Answer: Four main differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition —
| Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
|---|---|
| CO2, water and sunlight are used for photosynthesis. | Autotrophs are direct or indirect sources of food. Enzymes break down this type of food. |
| Chlorophyll is required in autotrophic nutrition. | Chlorophyll is not required in heterotrophic nutrition. |
| It comes from food which is prepared during day time. | It comes from food which is available all the time. |
| This type of nutrition is for all green plants and some bacteria. | This type of nutrition is for all animals and fungi. |
Question 2: Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Answer: Raw materials required for photosynthesis –
- Carbon dioxide – Plants get it from the atmosphere through stomata.
- Water – Plants absorb water from the soil through roots and transport to leaves.
- Sunlight – It is absorbed by the chlorophyll and other green parts of the plants
Question 3: What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
Answer: Acid makes an acidic medium in our stomach. This medium is necessary for the activation of the enzyme pepsin in the stomach. The acid also kills bacteria which the food may contain.
Question 4: What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer: Digestive enzymes such as lipase and pepsin break down the complex food molecules into simpler ones so that they can be absorbed by the walls of the intestine easily.
Question 5: How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
Answer: Small intestine has small projections called microvilli which increases the surface volume which makes absorption more effective. Within the villi there are numerous blood vessels that absorb digested food and carry it to the blood stream. Blood transports food to each part of our body.
End of Page no 87 solutions – In text exercise 2 – chapter number 5 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5.
Page 91
EX 3 – Chapter no 5 – Page 91 Solutions
Question 1: What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Answer: Aquatic organisms use oxygen dissolved in water which surrounds them. Since concentration of oxygen dissolved in water is very low, the aquatic organisms have a much faster rate of breathing to take sufficient oxygen. Terrestrial organisms take oxygen from the atmosphere which has oxygen with high concentration. This helps them to have much less breathing rate than aquatic organisms.
Question 2: What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms?
Answer: Glucose is first broken down in the cell cytoplasm into a three carbon molecule called pyruvate. Pyruvate is further broken down in the following ways to provide energy.
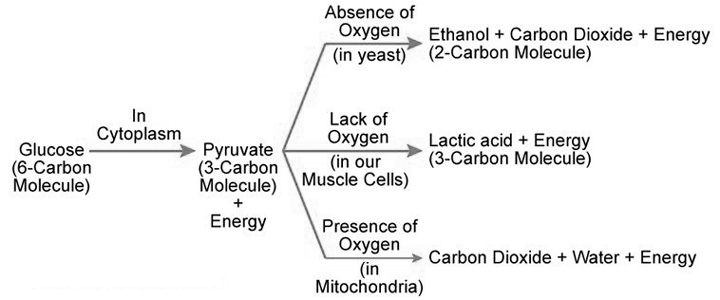
Question 3: How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Answer: Transport of oxygen – Blood capillaries use hemoglobin to absorb oxygen from the air in the lungs. It carries the oxygen to tissues which are deficient in oxygen before releasing it.
Transport of carbon dioxide – Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water. Therefore, it is mostly transported from body tissues in the dissolved form in our blood plasma to lungs. It is absorbed by the lungs alveoli from blood capillaries by diffusion.
Question 4: How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximise the area for exchange of gases?
Answer: The lungs have an air passage which is divided into smaller tubes, called bronchi which in turn form bronchioles. Balloon-like structures, called alveoli are present at the end of the bronchioles. The alveoli are where the lungs and the blood exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of breathing in and breathing out. The alveoli provide maximum surface for exchange of gases.
End of Page no 91 solutions – In text exercise 3 – chapter number 5 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5.
Page 96
EX 4 – Chapter no 5 – Page 96 Solutions
Question 1: What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Answer: Heart, blood and blood vessels are the main components of the transport system in human beings. The heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body parts and pumps it to lungs for enriching with oxygen. Blood transports oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide, hormones and nitrogenous waste. Blood vessels, arteries and veins carry blood to all parts of the human body.
Question 2: Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Answer: Mammals and birds are warm blooded animals. They produce more energy than energy produced by other animals in order to keep their body temperature constant. To produce a lot of energy, they require a lot of oxygen for more cellular respiration. Hence, it is important to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to meet the amount of oxygen required.
Question 3: What are the components of the transport system in highly organised plants?
Answer: Xylem and phloem are the two different types of conducting tissues which constitute transport system in highly organized plants. Xylem consists of vessels, tracheids and other xylem tissues while phloem is composed of various specialized cells called sieve elements, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma cells.
Question 4: How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Answer: Xylems parts tracheids and vessels of roots, stems and leaves are interconnected to form a continuous system of water-conducting channels that reaches all parts of the plant. Transpiration creates a suction pressure which forces water into xylem cells of roots. After this, there will be a steady movement of water from the root xylem to all parts of the plant connected through conducting interconnected water-conducting channels.
Question 5: How is food transported in plants?
Answer: The movement of food in phloem takes place by utilizing energy. The sugar made in leaves is loaded into the sieve tubes of phloem tissue by using energy from ATR. Water now enters the sieve tubes containing sugar by the process of osmosis due to which the pressure in the phloem tissue rises. This high pressure produced in the phloem tissue moves the food to all parts of the plant having less pressure in their tissues.
End of Page no 96 solutions – In text exercise 4 – chapter number 5 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5.
Page 98
EX 5 – Chapter no 5 – Page 98 Solutions
Question 1: Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
Answer: Structure of nephrons – Nephrons are the basic filtering units of kidneys. Each kidney possesses a large number of nephrons. The main components of the nephron are glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, and a long renal tubule.
Functioning of a nephron —
- The blood enters the kidney through the renal artery, which branches into many capillaries associated with glomerulus.
- The water and solute are transferred to the nephron at Bowman’s capsule.
- In the proximal tubule, some substances such as amino acids, glucose, and salts are selectively reabsorbed and unwanted molecules are added in the urine.
- The filtrate then moves down into the loop of Henle, where more water is absorbed.
- From here, the filtrate moves upwards into the distal tubule and finally to the collecting duct. Collecting duct collects urine from many nephrons.
- The urine formed in each kidney enters a long tube, called a ureter. From the ureter, it gets transported to the urinary bladder and then into the urethra.
Question 2: What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Answer: Plants use completely different strategies for excretion than those of animals. They can get rid of excess water by transpiration. For other wastes, plants use the fact that many of their tissues consist of dead cells, and that they can even lose some parts such as leaves. Many plant waste products are stored in cellular vacuoles. Waste products may be stored in leaves that fall off. Other waste products are stored as resins and gums, especially in old xylem. Plants also excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
Question 3: How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Answer: The amount of urine produced depends on the amount of excess water and dissolved wastes present in the body. Some other factors such as the habitat of an organism and hormones such as Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) also regulate the amount of urine produced.
End of Page no 98 solutions – In text exercise 5 – chapter number 5 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5.
Page 99
Chapter End Questions – Page 99 Solutions
Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
Answer: (c) excretion.
Question 2: The xylem in plants are responsible for
Answer: (a) transport of water.
Question 3: The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
Answer: (d) all of the above.
Question 4: The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
Answer: (b) mitochondria.
Question 5: How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
Answer: Fats are present in the form of large globules in the small intestine. The small intestine receives the secretions from the liver and the pancreas. The bile salts break down the large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzyme lipase can easily act on them. This is referred to as emulsification of fats. This process takes place in the small intestine.
Question 6: What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Answer: The saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase that breaks down starch which is a complex molecule to give simple sugar. It also moistens the food for easy swallowing.
Question 7: What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its byproducts?
Answer: The necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition are –
- Presence of chlorophyll in the living cells.
- Supply of water to green plants or cells of the plant.
- Sufficient sunlight.
- Sufficient carbon dioxide.
By-product of autotrophic nutrition is oxygen.
Question 8: What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
Answer: (i) Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen while anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
(ii) The products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide and water while the products of anaerobic respiration are ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
(iii) Aerobic respiration generates a considerable amount of energy while anaerobic respiration generates much less energy.
(iv) Aerobic respiration occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria while anaerobic respiration occurs only in cytoplasm.
Question 9: How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer: The alveoli are the small balloon-like structures present in the lungs. The walls of the alveoli consist of an extensive network of blood vessels. Each lung contains 300-350 million alveoli, making it a total of approximately 700 million in both the lungs. The alveolar surface when spread out covers about 80 m2 area. This large surface area makes the gaseous exchange more efficient.
Question 10: What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Answer: Haemoglobin is responsible for transporting oxygen to the body cells for cellular respiration. Deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies can affect the oxygen supplying capacity of blood. This can lead to deficiency of oxygen in the body cells. This can cause a disease called anemia.
Question 11: Describe double circulation of blood in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Answer: Blood enters twice to our heart and also pumped out twice from the heart. The deoxygenated blood from the body is brought to the right atrium through vena cava from where it is sent to the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, the blood is pumped to the lungs for oxygenation through the pulmonary artery. The oxygenated blood from lungs again enters the left atrium of the heart through pulmonary veins. From the left atrium it is sent to the left ventricle, from where this oxygenated blood is pumped to different parts of the body through the arteries.
This kind of separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood ensures a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body.
Question 12: What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Answer: Differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem –
- Xylem tissue helps in the transport of water and minerals while phloem tissue helps in the transport of food.
- Water is transported upwards from roots to all other plant parts in xylem while food is transported in both upward and downward directions in phloem.
- Transportation in xylem occurs with the help of physical forces such as transpiration pull while transportation in phloem requires energy in the form of ATP.
Question 13: Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Answer: Structure of alveoli – Alveoli are tiny balloon-like structures. Its walls are one cell thick. Alveoli contains an extensive network of blood capillaries.
Functioning of alveoli – The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place through the network of capillaries in alveoli.
Structure of nephrons – Nephrons are tubular structures. They are made of glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, and a long renal tube.
Functioning of nephrons – The Bowman’s capsule in nephron regulates the concentration of water and salts.
End of Page no 99 solutions – Chapter 5 Exercise 6 – Chapter end exercise. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5.
Ch 5 Ex 6 – Chapter end question answer.

