Find the Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 on our website with all the questions and answers especially written for class 10 students. You will know about Ch 4 Carbon and its Compounds, learn its concepts, and get important tips 🔥 on how to write (1) precise answers (2) without using unnecessary words (3) within ideal length. You will access all of this information for FREE in addition to class 10 science NCERT solutions chapter 4.
Ch 4 – Carbon and its Compounds

Use this link — 🌐 10.solutionsir.com for any kind of help in 10th class 2023-24. Click Here for » All Chapters: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Exercise – Food, clothes, medicines, books and many other things that we frequently use in our daily life are all based on a versatile element carbon. Interestingly, all living structures are also carbon based. ⚡ In the fourth chapter “Carbon and its Compounds” (Chapter 4 Science Class 10), we will study about some more interesting compounds and their properties. We will also learn about carbon, an element which is of immense significance to us in both its elemental form and in the combined form.
Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds – Important Points: Carbon is a versatile element that forms the basis for all living organisms and many of the things we use. This large variety of compounds is formed by carbon because of its tetravalency and the property of catenation that it exhibits. The ability of carbon to form chains gives rise to a homologous series of compounds in which the same functional group is attached to carbon chains of different lengths.
Special Note: 👉 Click the “Prepare” button to know, how to prepare Carbon and its Compounds chapter for exams. Get more helpful information, watch explanation videos and pay attention to handwritten version of our answer to score 💯 good marks in class 10 Science NCERT solutions Chapter 4. You will get everything that you need to prepare a question thoroughly.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4
Table of Contents
Page 61
EX 1 – Chapter no 4 – Page 61 Solutions
Question 1: What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
Answer: Electron dot structure of carbon dioxide (CO2) —
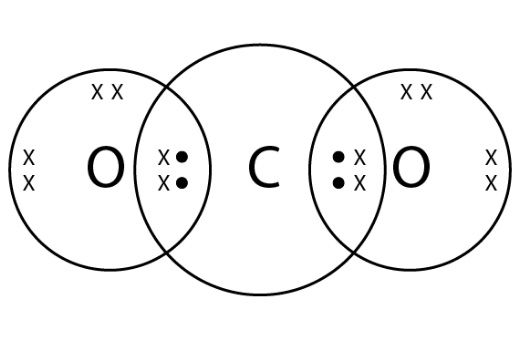
Question 2: What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (Hint – The eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring.)
Answer: Electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur —
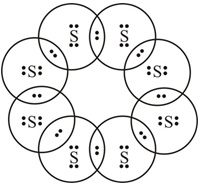
End of Page no 61 solutions – In text exercise 1 – chapter number 4 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4.
Page 68
EX 2 – Chapter no 4 – Page 68 Solutions
Question 1: How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Answer: 3 structural isomers are possible for pentane, as shown below —
(i) n-pentane — 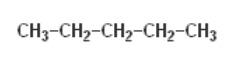
(ii) iso-pentane — 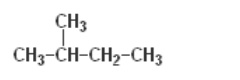
(iii) neo-pentane — 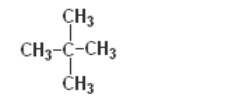
Question 2: What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Answer: Carbon forms huge number of compounds due to these two properties —
(i) Catenation, which refers to the ability of a carbon atom to make bonds with other carbon atoms.
(ii) Tetravalency, which refers to the property of carbon to form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms because it has 4 valence electrons.
Question 3: What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Answer: The molecular formula of cyclopentane — C5H10
Electron dot structure of cyclopentane —
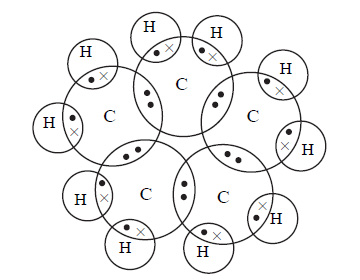
Page no 68 solutions continue on the next page. Scroll down for questions 4 and 5. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4.
Page 69
EX 2 – Chapter no 4 – Page 69 Solutions
Question 4: Draw the structures for the following compounds.
(i) Ethanoic acid
Answer: Structure of Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) —
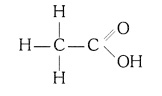
(ii) Bromopentane
Are structural isomers possible for bromopentane?
Answer: Three structural isomers are possible for Bromopentane (C5H11Br) —
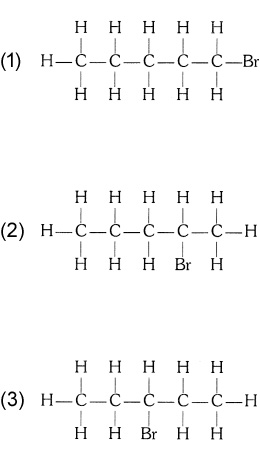
(iii) Butanone
Answer: Structure of Butanone (CH3CH2COCH3) —
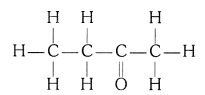
(iv) Hexanal
Answer: Structure of Hexanal (C5H11CHO) —
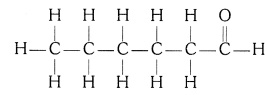
Question 5: How would you name the following compounds?
Answer: The name of the given compounds (i) CH3CH2Br (ii) HCHO (iii) CH3(CH2)3CHCH2 are —
| (i) | 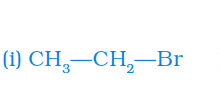 | Bromoethane |
| (ii) | 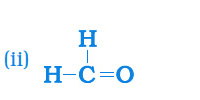 | Methanal |
| (iii) | Hexyne |
End of Page no 69 solutions – In text exercise 2 – chapter number 4 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4.
Page 71
EX 3 – Chapter no 4 – Page 71 Solutions
Question 1: Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Answer: Conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid is an oxidation reaction because the reaction involves the addition of oxygen to ethanol. The job of adding oxygen is done by oxidising agents such as alkaline potassium permanganate —
Question 2: A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Answer: Welding is done at a very high temperature which can be attained only when a mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt because the mixture gives a clean flame due to its complete combustion. A mixture of ethyne and air is not used for welding because it gives a sooty flame and low temperature. This happens because the limited supply of oxygen leads to incomplete combustion of the mixture.
End of Page no 71 solutions – In text exercise 3 – chapter number 4 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4.
Page 74
EX 4 – Chapter no 4 – Page 74 Solutions
Question 1: How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Answer: We can distinguish between alcohol and carboxylic acid by putting them to react with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates. Carboxylic acid reacts with carbonates and produces carbon dioxide gas which turns lime water milky whereas alcohol does not react with carbonates.
Question 2: What are oxidising agents?
Answer: Oxidising agents are the reactants which give oxygen to other substances or which remove hydrogen from a substance in a redox reaction.
End of Page no 74 solutions – In text exercise 4 – chapter number 4 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4.
Page 76
EX 5 – Chapter no 4 – Page 76 Solutions
Question 1: Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Answer: We cannot check if water is hard by using a detergent because a detergent forms lather in a similar way on reacting with both hard water and soft water.
Question 2: People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Answer: It is necessary to agitate the soap mixture because the soap micelles trap oily or greasy particles but still remain on the surface of our clothes. When the clothes are agitated or beaten, the micelles containing the dirt leave the surface of clothes and gets washed away with water.
End of Page no 76 solutions – In text exercise 5 – chapter number 4 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4.
Page 77
Chapter End Questions – Page 77 Solutions
Question 1: Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
Answer: (b) 7 covalent bonds.
Question 2: Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
Answer: (c) Ketone.
Question 3: While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
Answer: (b) the fuel is not burning completely.
End of Page no 77 solutions – Chapter 4 Exercise 6 – Chapter end exercise. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4.
Page 78
Chapter End Exercises – Page 78 Solutions
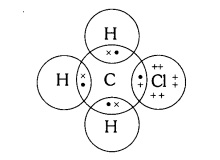
Question 4: Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer: CH3Cl completes its octet configuration by sharing its 4 electrons with three hydrogen atoms and one chlorine atom. Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. As a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and 1 bond with chlorine. See below —
Question 5: Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid
Answer: Electron dot structure for Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) –
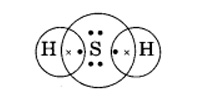
(b) H2S
Answer: Electron dot structure for Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) –
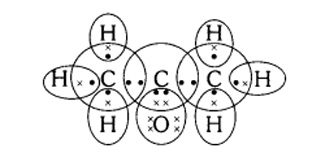
(c) propanone
Answer: Electron dot structure for Propanone (CH3COCH3) –
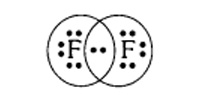
(d) F2
Answer: Electron dot structure for Fluorine (F2) –
Question 6: What is an homologous series? Explain with an example.
Answer: A homologous series is a family of hydrocarbons with the same functional group and same general formula but different numbers of some repeated groups such as CH2. For example, Methane CH4, Ethane CH3CH3, Propane CH3CH2CH3, Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3 etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series.
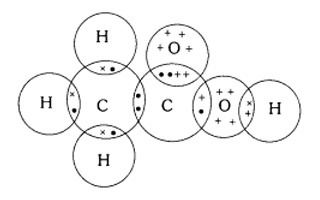
Question 7: How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer: Ethanol and Ethanoic acid can be differentiated on the basis of their following properties —
1 – Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature with a pleasant smell while ethanoic acid has a melting point of 17°C which is below the room temperature. so, ethanoic acid freezes during winter. Also, ethanoic acid has a smell like vinegar.
2 – Ethanol does not react with metal carbonates while ethanoic acid reacts with metal carbonates to form salt, water and carbon dioxide. For example –
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 ⟶ 2CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
3 – Ethanol does not react with NaOH while ethanoic acid reacts with NaOH to form sodium ethanoate and water. For example –
CH3COOH + NaOH ⟶ CH3COONa + H2O
4 – Ethanol is oxidized to give ethanoic acid in presence of acidified KMnO4 while no reaction takes place with ethanoic acid in presence of acidified KMnO4.
Question 8: Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Answer: Micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water because the hydrocarbon chains of soap molecules are hydrophobic (water repelling) which are insoluble in water, but the ionic ends of soap molecules are hydrophilic (water attracting) and hence soluble in water. Such micelle formation will not be possible in other solvents like ethanol in which sodium salt of fatty acids do not dissolve.
Question 9: Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Answer: Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels for most applications because they have high calorific values and give a lot of heat and light when burnt in air.
Question 10: Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer: Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. When hard water is treated with soap, an insoluble precipitate or scum is formed in this reaction. Presence of calcium and magnesium in hard water leads to less formation of lather and thus some amount of salt is unused.
Question 11: What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer: The soap is basic in nature. So, on testing the soap with litmus paper, red litmus turns blue and blue litmus remains unchanged.
Question 12: What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer: Hydrogenation is a process or a chemical reaction between hydrogen and other compounds. It is usually done in the presence of catalysts, for example – nickel, palladium or platinum. Hydrogenation is used mainly to saturate organic compounds.
Question 13: Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions:
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer: Addition reactions take place only in unsaturated hydrocarbons. So addition reaction takes place only in C3H6 and C2H2.
Question 14: Give a test that can be used to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Answer: Butter contains saturated fats. Therefore, it cannot be hydrogenated. On the other hand, oil has unsaturated fats. That is why it can be hydrogenated to saturated fats.
Question 15: Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer: The nature of dirt on clothes is organic and insoluble in water. Because of its stickiness, it cannot be removed completely by only washing with water. When soap is added to water, its molecules and their two ends help to remove the dirt easily. The hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and dirt leaves the surface of clothes. These molecules form a micelle formation and trap the dirt at the center. Then, the dust particles are rinsed away with the help of the water.
End of Page no 78 solutions – Ch 4 Ex 6 – Chapter end question answer. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4.

