Find the Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 on our website with all the questions and answers especially written for class 10 students. You will know about Ch 2 Acids, Bases and Salts, learn its concepts, and also have access to important tips 🔥 on how to write (1) precise answers (2) without using unnecessary words (3) within ideal length. You will access all of this information for FREE in addition to class 10 science NCERT solutions chapter 2.
Ch 2 – Acids, Bases and Salts

Use this link — 🌐 10.solutionsir.com for any kind of help in 10th class 2023-24. Click Here for » All Chapters: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Exercise – Acids are sour in taste and change the colour of blue litmus to red, whereas bases are bitter and change the colour of the red litmus to blue. ⚡ In the second chapter “Acids, Bases and Salts” (Chapter 2 Science Class 10), we will understand the reactions of acids and bases, and how acids and bases cancel out each other’s effects. We will also learn about salt which is a chemical compound that is formed when a part of an acid is replaced by a metal or metal-like substance.
Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts – Important Points: Acid-base indicators are dyes or mixtures of dyes which are used to indicate the presence of acids and bases. Acidic nature of a substance is due to the formation of H+(aq) ions in solution. Formation of OH–(aq) ions in solution is responsible for the basic nature of a substance. Acidic and basic solutions in water conduct electricity because they produce hydrogen and hydroxide ions respectively.
Special Note: 👉 Click the “Prepare” button to know, how to prepare Acids, Bases and Salts chapter for exams. Get more helpful information, watch explanation videos and pay attention to handwritten version of our answer to score 💯 good marks in class 10 Science NCERT solutions Chapter 1. You will get everything that you need to prepare a question thoroughly.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2
Table of Contents
Page 18
EX 1 – Chapter no 2 – Page 18 Solutions
Question 1: You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Answer: We know that the basic solution changes the colour of red litmus paper to blue and acidic solution turns blue litmus paper red. So –
Step 1 – We will put the red litmus paper in all the three test tubes turn by turn until the change occurs. The test tube which turns the red litmus paper to blue, should be eliminated and marked as Basic Solution.
Step 2 – Now, we are left with two test tubes and blue litmus paper whose original colour was red. Put the blue litmus paper in any one test tube. It contains either acidic solution or distilled water. If the blue litmus changes to red, the test tube should be marked as Acidic Solution. If there is no change, the test tube should be marked as Distilled Water.
Step 3 – The last test tube should be marked as Distilled Water if we have got the acidic solution in step 2. Or – it should be marked as Acidic Solution if we have got distilled water in step 2. We can confirm it by putting the blue litmus paper in the last test tube which would turn blue litmus red.
End of Page no 18 solutions – In text exercise 1 – chapter number 2 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Page 22
EX 2 – Chapter no 2 – Page 22 Solutions
Question 1: Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Answer: Curd and sour substances contain acids which produce salt and hydrogen gas on reacting with metals –
Acid + Metal ⟶ Salt + Hydrogen gas
When sour foods are kept in metal containers like brass and copper vessels, the above reaction occurs to form harmful gases and compounds which spoil our foods and make them unhealthy. So, curd and sour substances should not be kept in brass and copper vessels.
Question 2: Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Answer: Hydrogen gas (H2) is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal. For example, sulphuric acid reacts with zinc to produce zinc sulfate salt along with hydrogen gas –
H2SO4 + Zn ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2
We can test for the presence of hydrogen gas by setting up an apparatus as shown in the drawing below –
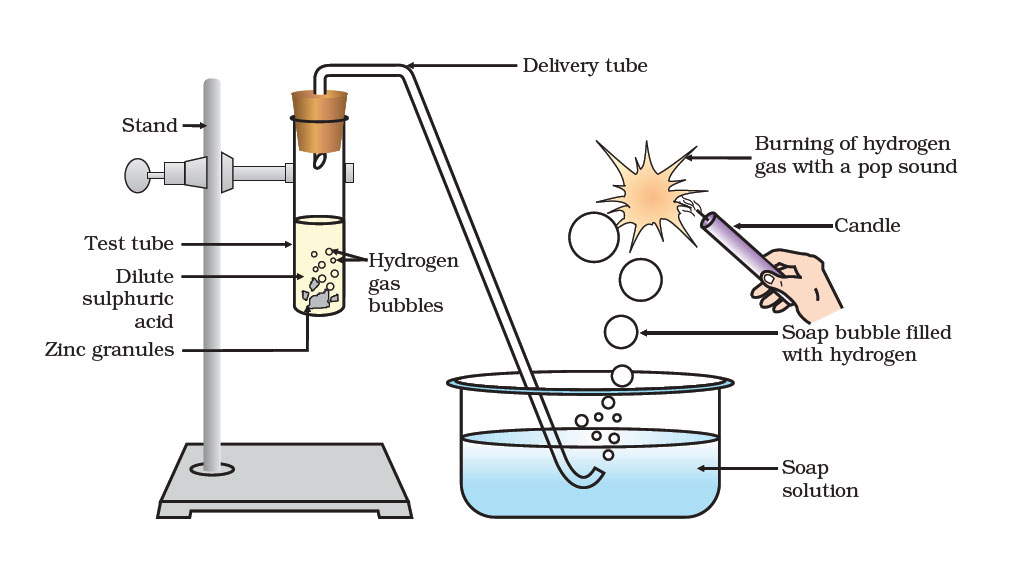
Test for hydrogen gas – We have a small amount of dilute sulphuric acid in a test tube. Add some pieces of zinc granules to it. This reaction produces a gas which goes through a delivery tube and then passes through the soap solution. You can understand by looking at the diagram how the apparatus helps us to trap the gas inside soap bubbles which go up in the air.
Now, bring a burning candle near a rising bubble. The gas which is trapped in the bubble, burns quickly and the bubble bursts with a pop sound. This activity confirms the presence of hydrogen gas in soap bubbles.
Question 3: Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Answer: One of the compounds formed in this displacement reaction is calcium chloride and the gas evolved is carbon dioxide because it extinguishes the burning candle. Considering these facts, we can conclude that reactant A is calcium carbonate –
CaCO3 + 2HCl ⟶ CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
End of Page no 22 solutions – In text exercise 2 – chapter number 2 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Page 25
EX 3 – Chapter no 2 – Page 25 Solutions
Question 1: Why do HCl, HNO3, etc., show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Answer: We know that acids give hydronium ions (H3O+) in water. Compounds like HCl or HNO3 also give hydronium ions (H3O+) in water because hydrogen ions (H+) separate from HCl or HNO3 in the presence of water and then combine with water to form hydronium ions –
HCl + water ⟶ H+ + Cl– + water
H+ + Cl– + H2O ⟶ H3O+ + Cl–
This is why HCl or HNO3 shows acidic characters in aqueous solutions. Solutions of alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character because the hydrogen element does not separate from these compounds in the presence of water. As a result, hydrogen ions or hydronium ions are not formed.
Question 2: Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Answer: The conduction of electricity is the movement of charged particles. Acids when combined with water, release ions which are charged particles. These ions move independently in aqueous solution. For this reason, an aqueous solution of an acid conducts electricity.
Question 3: Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
Answer: Hydrogen ions (H+) are responsible for the colour change of litmus paper. Acidic solutions change the colour of litmus paper because acids form hydrogen ions when combined with water. Hydrogen ions are not produced in the absence of water. For this reason, dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
Question 4: While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Answer: The process of dissolving an acid in water is a highly exothermic one. When water is added into concentrated acid, a huge amount of heat is released all of a sudden. In this method, the solution boils violently, splashes out and can even cause burns on body parts. In order to avoid such accidents, acid should be added to water. In this method, water absorbs most of the heat and the solution releases very little heat which cannot do more than warm the solution.
Question 5: How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
Answer: When a solution of an acid is diluted by mixing it with water, the number of hydronium ions (H3O+) per unit volume decreases. In simple words, the concentration of hydronium ions decreases and the strength of the acid also decreases.
Question 6: How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Answer: When excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide, the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) per unit volume increases. Consequently the solution becomes concentrated and the strength of the base increases.
End of Page no 25 solutions – In text exercise 3 – chapter number 2 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Page 28
EX 4 – Chapter no 2 – Page 28 Solutions
Question 1: You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer: Solution A has more hydrogen ion concentration than solution B has because smaller pH value means more number of hydronium ions per unit volume. Also, solution A is acidic and solution B is basic because solutions with pH value less than 7 indicate more hydrogen ion (H+) concentration (acidic nature) while solutions with pH value greater than 7 indicate more hydroxide ion (OH–) concentration (basic nature).
Question 2: What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Answer: The concentration of H+ ions in a solution is responsible for making the solution acidic or basic. If the concentration of H+ ions increases, the solution becomes more acidic. If the concentration of H+ ions decreases, the solution becomes less acidic causing an increase in the basic nature of the solution. In addition, a solution is said to be neutral when the concentration of H+ ions is equal to the concentration of OH– ions.
Question 3: Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Answer: Yes, basic solutions also have H+ ions but these solutions still show basic nature because the presence of H+ ions or OH– ions does not decide the nature of the solution. It is the number of H+ ions per unit volume or the H+ ion concentration which makes the solution acidic or basic. Basic solutions have more concentration of OH– ions than that of H+ ions.
Question 4: Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Answer: If the soil is acidic in nature (with low pH value), it impacts agricultural productivity badly. In this case, farmers should treat his fields with a good base such as quick lime, slaked lime or chalk. It would help them to balance the pH value of soil and make the fields favourable to plant growth.
End of Page no 28 solutions – In text exercise 4 – chapter number 2 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Page 33
EX 5 – Chapter no 2 – Page 33 Solutions
Question 1: What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2?
Answer: Bleaching powder.
Question 2: Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Answer: Calcium hydroxide or Ca(OH)2.
Question 3: Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Answer: Washing soda or Na2CO3.10H2O
Question 4: What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Answer: On heating the solution of sodium hydrocarbonate, sodium carbonate and water is produced along with the evolution of carbon dioxide gas.
Question 5: Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Answer: On mixing with water, Plaster of Paris changes to gypsum –
⟶⟶
End of Page no 33 solutions – In text exercise 5 – chapter number 2 intext questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Page 34
Chapter End Questions – Page 34 Solutions
Question 1: A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
Answer: (d) 10
Question 2: A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains
Answer: (b) HCl
Question 3: 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be
Answer: (d) 16 mL
Question 4: Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
Answer: (c) Antacid
Question 5: Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when –
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
Answer: Dilute sulphuric acid + Zinc ⟶ Zinc Sulphate + Hydrogen
H2SO4 + Zn ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
Answer: Dilute hydrochloric acid + Magnesium ⟶ Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
2HCl + Mg ⟶ MgCl2 + H2
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
Answer: Dilute sulphuric acid + Aluminium ⟶ Aluminium sulphate + Hydrogen
3H2SO4 + 2Al ⟶ Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
Answer: Dilute hydrochloric acid + Iron ⟶ Ferrous chloride + Hydrogen
6HCl + 2Fe ⟶ 2FeCl3 + 3H2
Question 6: Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an Activity to prove it.
Answer: Activity – Fix two iron nails on a piece of cork, and place the cork in a 100 mL beaker. Connect the nails to the two terminals of a 6 volt battery through a bulb and a switch, as shown in the drawing below.
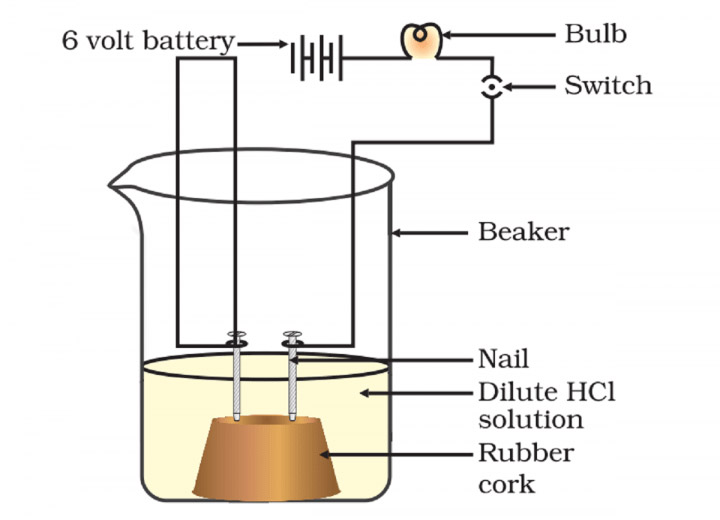
Now pour some (i) dilute hydrochloric acid in the beaker and switch on the current. The bulb glows. Empty the beaker to repeat the activity with (ii) dilute sulphuric acid, (iii) alcohol solution and then (iv) glucose solution in the end.
Observations – The bulb glows in the case of acid solutions but does not glow in case of alcohol solution or glucose solution. Acids conduct electricity but alcohol or glucose solution does not.
Result – Acids dissociate into ions in aqueous solutions and these ions carry electric current through the solution. Since the cation present in acids is H+, acids produce hydrogen ions (H+) in solution. Alcohol and glucose solutions do not conduct electricity because they do not produce hydrogen ions.
Conclusion – Release of hydrogen ions in aqueous solution is a common property of acids. Alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids because they don’t release hydrogen ions in aqueous solution, as seen in the above activity.
Question 7: Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does?
Answer: Distilled water is a pure form of water which does not contain ions responsible for flow of electric current. Hence, it does not conduct electricity. Rainwater, on the other hand, becomes acidic while falling on the earth because carbon dioxide in the air reacts with raindrops to form carbonic acid. This is why rainwater contains ions and thus conducts electricity.
End of Page no 34 solutions – Chapter 2 Exercise 6 – Chapter end exercise. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2.
Page 35
Chapter End Exercises – Page 35 Solutions
Question 8: Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Answer: Acids show acidic behaviour because of their property of releasing hygrogen ions (H+) readily. If hydrogen ions do not separate from acids, acidic behaviour remains missing. But hydrogen ions can only be produced (or separated from acids) in the presence of water. In other words, acids require water to show their acidic behaviour.
Question 9: Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9, respectively. Which solution is
(a) neutral?
Answer: Solution D is neutral.
(b) strongly alkaline?
Answer: Solution C is strongly alkaline.
(c) strongly acidic?
Answer: Solution B is strongly acidic.
(d) weakly acidic?
Answer: Solution A is weakly acidic.
(e) weakly alkaline?
Answer: Solution E is weakly alkaline.
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
Answer: pH values in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration —
11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1
Question 10: Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Answer: The fizzing will occur more vigorously in test tube A because hydrochloric acid (HCl) produces hydrogen gas (H2) at a faster rate than acetic acid (CH3COOH), on reacting with magnesium. It is because hydrochloric acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid, and also contains more hydrogen ions (H+) to generate than acetic acid.
Question 11: Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Answer: The pH of milk reduces and gets lower than 6 as the milk turns into curd because in this process, lactic acid is formed in the curd. Lactic acid makes the curd acidic and reduces its pH.
Question 12: A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a)Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
Answer: The pH of milk changes over time. As the time passes, the pH value goes down and the milk becomes more acidic. This makes the milk sour. The milkman adds baking soda to fresh milk to shift the pH because by increasing the pH of milk from 6 to alkaline, he can keep the milk from being acidic and becoming sour, for a longer time.
(b)Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Answer: Lactic acid formed in milk is responsible for turning milk into curd over time. But the alkaline milk takes a longer time to set as curd because lactic acid, initially formed, is completely consumed by the alkaline milk to neutralise the alkali present in milk. Lactic acid, formed afterwards, is used for curdling of neutralised milk.
Question 13: Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Answer: Plaster of Paris, a powdery mass, absorbs water from moisture to start hydration reaction and quickly sets to a hard mass, known as gypsum. So, the plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container to prevent it from setting to a hard mass.
Question 14: What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Answer: A reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to give salt and water, is known as a neutralisation reaction.
Example (1) : HCl + NaOH ⟶ NaCl + H2O
Example (2) : H2CO3 + Mg(OH)2 ⟶ MgCO3 + 2H2O
Question 15: Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Answer: 2 important uses of washing soda –
(i) It is used in glass, soap and paper industries.
(ii) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
2 important uses of baking soda –
(i) It is used as an antacid which helps to neutralize excess acid in the stomach and provides relief.
(ii) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
End of Page no 35 solutions – Ch 2 Ex 6 – Chapter end question answer. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2.

